You probably know experts who state that standardization is critical for work and information processes. They dogmatically declare that you get reduced variability, cost reduction, better quality, and consistency across the organization with standardization. In fact if you don’t have standardization you can’t make improvements because people and business units do the process differently to start!
Yet, on the other side there are experts that say that flexibility is critical, the only way to stay current in the market place, to satisfy varying customer needs. Flexibility allows your process to respond to specific demands, to be agile, to use the human decision making that is necessary in so many decisions.
This article will address
- When should you have standard processes vs. flexible processes?
- How do you get the two different camps to talk to one another and find the best solution?
- Is this an either/or decision or can the two conditions live together?
First, let’s agree on some definitions. Standardization of work and information processes can take many forms. At the basic level, standardization means that processes have exactly the same steps, in the same sequence, and completed by the same roles for all units doing the process. At an even more stringent level standardization means that the process runs at the same speed and maintains a stated level of inventories. There is no variability between processes across units and there is no variability in the process on Monday vs. Tuesday vs. Wednesday.
Flexibility on the other hand means that the work process is different under varying conditions, and these conditions created the need for differences. The most obvious need is a difference in customer type which demands a different output from the process from the commoditized standardized process. The customer might demand a different level of service or different elements in the product.
So how do you know which is more important for your process – standardization or flexibility?
Recently, probably because of the recession, I have had a lot of clients asking me to help them standardize their processes. Let me give you a few different examples. One client asked me to help them standardize their recruiting and hiring processes. The VP of Human Resources told me there were 15 different recruiting and hiring processes in the 4 divisions of the company. It took anywhere from 3 months to 18 months to hire employees; they did not know where candidates were in the hiring process; and she was not sure how many staff she needed to do the work. Additionally the process was paper intensive, hiring managers felt recruiters did not understand their needs, and the process had burdensome compliance requirements. She asked me to help her standardize the process.
The VP of Human Resources kicked off the initiative and explained the current challenges and her goals. She helped form teams to model how the process was done in the different divisions and to formulate improvement ideas for a new standardized process. As I started working with her organization, I found that most people were opposed to the idea of ‘standardization’. It sounded like “Big Brother” and it sounded as though many of their special needs would not be met. I began to tell employees and managers that standardization did not necessarily mean we would have only one process that everyone would follow but rather that we would move to more consistent ways of doing recruiting and hiring across the whole organization. If there were reasons to have a few different hiring processes we would recommend that. In fact as we finished the project there were many aspects of the new process that were standardized across the whole company – templates for candidate information, the same computer application, fewer HR roles, a single point of contact in HR for the hiring manager, job descriptions housed in a single database, templates for recruiting plans., and timing expectations. But there was not just one standardized process – instead there were three processes, one for hiring scientists, another for hiring summer interns, and a third for all other employees.
In another situation I was asked to help standardize the way an organization did procurement. This project was part of an enterprise effort to streamline the process, utilize one method across the organization, and apply the new eProcurement software application they had recently installed. We asked 35 different business units to come together to map how they currently did the procurement process, determine what flow and information they needed, and agree on one way that would work at the 80% level for the organization. We found that
- Once each organization had mapped how it currently did its process, it was quite easy to compare to the other 34 processes and determine what was similar and what was different across the group.
- The IT department had neglected to understand some of the critical features needed for each business unit- mostly around (1) providing some ability for the unit to make changes themselves when they discovered errors, and (2) to see – have transparency – where the request was in the process, when the invoice came from the vendor, or to know if the payment had been made.
- Different units – depending on the type of request they made (such as need for speed, special medical requests, or because of the large volume of purchases) had some requirements that were validly different.
- Although the customized department procurement and tracking systems had grown out of individual unit needs, many of units required specific categorized information to meet their fund accounting requirements. If the new eProcurement system could not provide this information, they would need to maintain their own department systems as well or revert to more time intensive manually tracking.
Here’s a third example: The Finance group wanted to standardize the way 12 different units handled the budget process and improve the level of analysis that they were able to do. They began by creating a current state map for one of the units and tried to abstract the other 11 units from there. But everyone thought ‘theirs was different.’ So they developed 12 different “as is” maps of the budget process, one for every unit. Then they looked at them–and voila– it was pretty evident what steps were the same and which were different.
Often in talking about their processes or in developing their own ‘as is’ maps groups use different terms for similar elements, so clarifying language is an important first step. Secondly, units may use different roles to do different steps, and different roles may necessitate different skills levels, which can explain why some roles perform more or less steps. Third, units may do steps in a different order for logical reasons or just because they have always done it that way. Each of these three differences is minor. As the budget units looked at their 12 maps they were able to create one consolidated ‘as is’ map. And they had learned best practices in their study of the 12 groups.
Then as they analyzed the wastes and pain points together on the consolidated map ‘as is’ map they had a lot of goals in common—they wanted to stop re-entering data from the enterprise system, they wanted to agree on terms and data definitions, and they wanted to reduce the administrative work and rework. As they thought about the future state map, they found a best practice in another part of the organization which enabled them to eliminate all their ‘translator” excel spreadsheets. They came up with both short term and longer term solutions and put the time saved per analyst toward the value added step of financial analysis. Thy formed a community of practice to decide what analysis was most important for their customers. The team moved from 12 positional silos to one common goal, they redesigned the process into one common process, and they became a strong professional group emphasizing their value added skills.
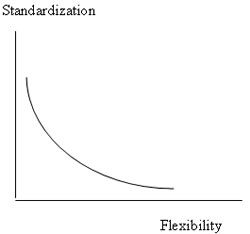 |
It is true that the more standarization you have the less flexibility you have but there are many places on the curve where you can have a combination of each. And I assert that you need to have both. Standardization and flexibility are both strategies for maximizing return and they bring different results, but you need to consider both to get the best result for the customer and the organization. |
Let’s look at the benefits of each: standardization and flexibility
|
Benefits of
|
|
|
Standardization
|
Flexibility
|
| Repeatability Consistency across units Means to gather conforming information Quality Cost Easier for training personnel Easier to implement changes Eliminates variability in steps and outcomes |
Ability to respond to different customer requirements Ability to alter processes based on specific needs Agility – in marketplace Ability to meet different geographic or cultural needs Allows for use of different decision models Allows for experienced human input with special cases |
Standardization and flexibility are both important in understanding and improving your processes. Standardization moves the needle toward a single method, process, and outcome. Flexibility provides for variation where the customer situation requests it and it make sense for the business. Both can differentiate a product in the marketplace, one more for price and consistency and the other more for distinctive customer requirements. In order to get to the best combination, and to get both sides seeing the common goal, it is best to look at several instances of the way the process is done today, see what is the same and what is different, and standardize where you can but keep distinctions where different processes and different approaches make sense for special customer requirements.

















